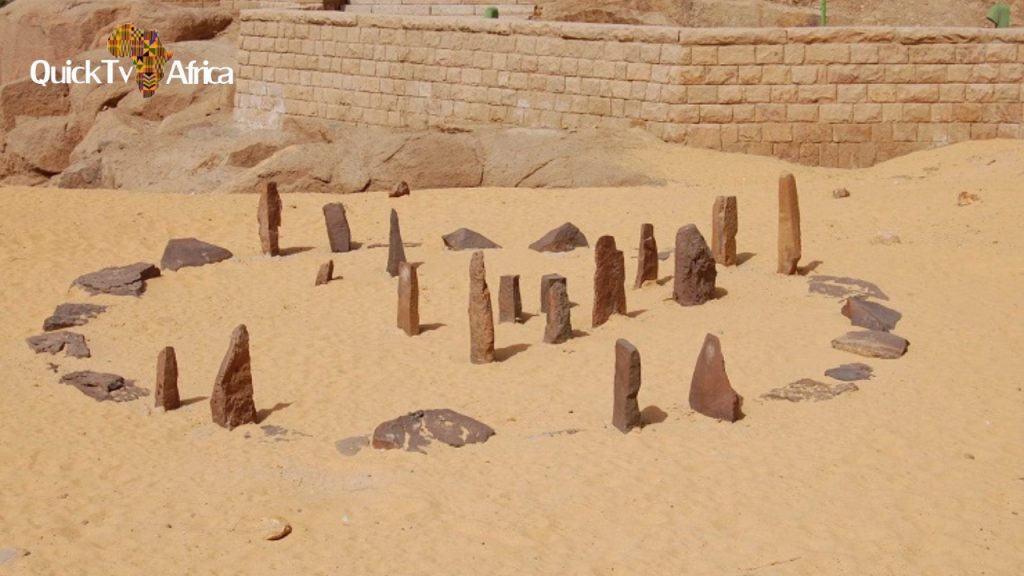
Nabta Playa: An Ancient Wonder Hidden in the Sahara
Deep in Egypt’s Sahara Desert, near the Nubian border, lies Nabta-Playa, an extraordinary archaeological site that challenges what we know about early civilizations. This 4,000-year-old stone circle—older than Stonehenge and other famed megalithic structures—served as both a ceremonial center and an astronomical calendar. Although Nabta Playa remains lesser-known than other ancient landmarks, it offers an incredible window into early African astronomy, spirituality, and ingenuity.
Discovering Nabta Playa: A Civilization in the Sand
Archaeologists stumbled upon Nabta Playa in the 1970s, uncovering evidence that it was once a thriving settlement. Thousands of years ago, this area was not the dry, lifeless desert we see today; it was a lush savanna with seasonal lakes that sustained communities of nomadic herders. For reasons not entirely understood, these people began constructing megalithic structures that align precisely with celestial bodies, making Nabta Playa one of the earliest known astronomical sites in the world.
The Stone Circles and Megaliths: A Prehistoric Observatory
The heart of Nabta Playa’s mystery lies in its circular arrangement of stones, some of which weigh several tons. These stone circles and upright monoliths were carefully positioned to align with the summer solstice. This alignment would have allowed ancient astronomers to predict the annual rainy season, a critical skill for communities that depended on rainfall to survive in such an arid region.
Beyond its use as a calendar, Nabta Playa also likely held spiritual significance. Many experts believe that the stones symbolized the connection between the Earth and the cosmos, indicating a sophisticated belief system that blended science with spirituality. In this way, Nabta Playa demonstrates that these early Africans not only understood astronomy but also held a complex worldview that honored their environment and the forces shaping it.
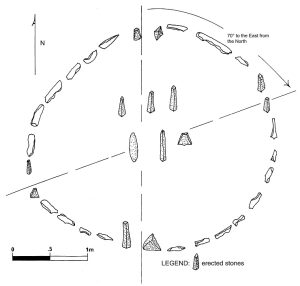
The Astounding Engineering of Nabta Playa
The stones at Nabta Playa aren’t simply scattered—they are meticulously arranged, suggesting that the people who created this site possessed advanced engineering skills. Moving the massive stones required extensive manpower and resources, indicating a well-organized society with leaders capable of mobilizing large groups.
Additionally, certain stones appear to form “gates” and “avenues” that may have been used in ceremonial processions. This implies a deep-rooted social and ritual structure in the community, reflecting an intricate blend of practical science and spiritual significance.
The People of Nabta Playa: Who Were They?
The people behind Nabta Playa were likely pastoralists—cattle herders who migrated across the Sahara. Evidence suggests that they lived in harmony with the land, following seasonal patterns and integrating celestial observations into their daily lives. These pastoralists possibly traveled widely, and some theories propose that they influenced or contributed to later cultures along the Nile, including the ancient Egyptians.
Artifacts from the site suggest that Nabta-Playa’s people had trade connections with other groups, and they may have exchanged knowledge of astronomy, agriculture, and animal husbandry. While much remains unknown, Nabta Playa’s creators undoubtedly represent one of Africa’s earliest societies with an advanced understanding of their environment.
Nabta Playa’s Legacy and Its Place in African History
Today, Nabta stands as a testament to the ingenuity of early African societies. Its presence predates Stonehenge and the Great Pyramids, underscoring Africa’s significant contributions to early human civilization. The site challenges Eurocentric narratives by proving that complex knowledge systems—particularly in science and astronomy—flourished in Africa long before other parts of the world.
Nabta also reshapes our understanding of human development. It suggests that early societies in Africa were far more organized and sophisticated than previously thought. Through its careful alignment with the cosmos, Nabta Playa exemplifies how ancient Africans not only observed the stars but built monuments in harmony with them, grounding their lives and beliefs in a profound connection with the universe.
Visiting Nabta Playa: A Journey into Deep History
While Nabta lies in a remote region, modern explorers and archaeology enthusiasts can visit with specialized tours that traverse the Sahara. For those who make the journey, the site provides a chance to experience the quiet strength of a civilization long past, where stones and sand whisper stories of our ancient connection to the stars.
Conclusion: Nabta Playa—A Wonder of the Ancient World
Nabta Playa remains one of Africa’s most awe-inspiring historical treasures. Its stone circles and megaliths, crafted by hands thousands of years ago, remind us of humanity’s enduring curiosity and spiritual connection to the cosmos. Though obscured by time and desert sands, Nabta Playa’s legacy continues to speak to the incredible ingenuity of early African societies and their lasting impact on human history.

